Best Waterproofing Membrane for Basement Walls
Basements, being subterranean structures, are inherently susceptible to moisture intrusion. The hydrostatic pressure exerted by groundwater against basement walls can lead to leaks, dampness, and ultimately, significant structural damage. Consequently, selecting and installing an effective waterproofing membrane is paramount in mitigating these risks and ensuring a dry, healthy basement environment. This article examines various waterproofing membrane options suitable for basement walls, outlining their characteristics, applications, and relative advantages and disadvantages to assist in making an informed decision.
Several factors must be considered when selecting a waterproofing membrane. These include the existing condition of the basement walls, the type of soil surrounding the foundation, the local water table level, and the anticipated budget for the project. Ignoring these factors can lead to the selection of an inappropriate system, resulting in costly repairs and continued moisture problems.
Understanding the Types of Waterproofing Membranes
Waterproofing membranes for basement walls are broadly classified into several categories, each with its own set of properties and application methods. These include, but are not limited to, liquid-applied membranes, sheet membranes, and cementitious coatings. Choosing the appropriate type depends on the specific challenges presented by the basement environment and the desired level of protection.
Liquid-Applied Membranes: These membranes are typically composed of polymers such as polyurethane, asphaltic rubber, or acrylics. They are applied in liquid form, either by brush, roller, or spray, and cure to form a seamless, flexible barrier against water penetration. Liquid-applied membranes are effective in sealing cracks and irregularities in concrete surfaces, making them suitable for existing basements with minor imperfections. They offer excellent adhesion and conformability, ensuring comprehensive coverage even in complex geometries.
However, the performance of liquid-applied membranes is highly dependent on proper surface preparation. The substrate must be clean, dry, and free of any loose particles or contaminants. Multiple coats may be required to achieve the desired thickness and waterproof integrity. Furthermore, some liquid-applied membranes may be sensitive to ultraviolet (UV) exposure, necessitating the application of a protective topcoat if exposed to sunlight.
Sheet Membranes: Sheet membranes are pre-manufactured waterproofing materials available in rolls. Common types include self-adhesive bitumen membranes, ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber, and thermoplastic polyolefin (TPO) membranes. These membranes are adhered to the basement wall surface, creating a physical barrier against water ingress. Sheet membranes offer consistent thickness and controlled quality, simplifying the installation process and reducing the risk of errors. They are particularly well-suited for new construction projects where the basement walls are relatively smooth and uniform.
Self-adhesive bitumen membranes are a widely used option due to their ease of installation and excellent waterproofing properties. They consist of a bitumen compound reinforced with a carrier fabric, such as fiberglass or polyester. The self-adhesive backing eliminates the need for separate adhesives, streamlining the application process. EPDM rubber membranes are known for their exceptional durability and resistance to weathering, chemicals, and UV radiation. TPO membranes offer superior resistance to punctures and tears, making them suitable for challenging soil conditions.
The key to successful sheet membrane installation lies in proper seam sealing. Overlapping seams must be thoroughly sealed to prevent water from penetrating through the joints. Specialized sealants and heat-welding techniques may be required to ensure watertight integrity.
Cementitious Coatings: Cementitious waterproofing coatings are composed of cement, aggregates, and chemical additives that react to form a waterproof barrier. These coatings are typically applied in multiple layers to achieve the desired thickness and protection. Cementitious coatings are cost-effective and easy to apply, making them a popular choice for interior basement waterproofing. They are particularly effective in preventing water vapor transmission, reducing the risk of condensation and mold growth.
Cementitious coatings are generally more rigid than liquid-applied or sheet membranes, making them less suitable for basements with significant structural movement or cracking. They may also require periodic reapplication to maintain their waterproof integrity. However, cementitious coatings offer excellent resistance to chemical attack and abrasion, making them a durable option for interior basement walls.
Application Considerations for Waterproofing Membranes
The success of any waterproofing system hinges on proper application techniques. Regardless of the type of membrane selected, meticulous surface preparation is essential. This includes cleaning the basement walls to remove any dirt, debris, or loose particles. Cracks and imperfections should be repaired using appropriate patching compounds before applying the membrane. The surface must be dry and free of any standing water or moisture.
For liquid-applied membranes, the manufacturer's instructions regarding mixing ratios, application rates, and curing times must be strictly followed. Multiple coats may be required to achieve the desired thickness and waterproof integrity. Ensure adequate ventilation during application, as some liquid-applied membranes may emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Sheet membrane installation requires precise alignment and overlapping of seams. Use a roller or squeegee to ensure proper adhesion to the substrate. Seams should be thoroughly sealed using appropriate sealants or heat-welding techniques. Pay particular attention to corners, edges, and penetrations, as these are common areas for water leakage.
Cementitious coatings should be mixed according to the manufacturer's instructions, ensuring a consistent and homogeneous consistency. Apply the coating in multiple thin layers, allowing each layer to dry before applying the next. Use a brush, roller, or trowel to achieve a smooth and uniform finish.
Furthermore, consider the ambient temperature and humidity during application. Extreme temperatures or high humidity levels can affect the curing time and performance of the waterproofing membrane. Consult the manufacturer's recommendations for optimal application conditions.
Key Factors in Choosing the Right Membrane
The selection of the most appropriate waterproofing membrane involves carefully assessing several critical factors relevant to the specific basement environment and project requirements. These factors are not universally applicable; rather, their relative importance varies based on the conditions present.
Soil Type and Hydrostatic Pressure: The type of soil surrounding the basement foundation directly influences the amount of hydrostatic pressure exerted against the walls. Clay soils, for instance, retain more water than sandy soils, resulting in higher hydrostatic pressure. In areas with high water tables or poorly drained soils, a robust waterproofing system capable of withstanding significant hydrostatic pressure is essential. Sheet membranes, particularly those reinforced with high-strength fabrics, are often preferred in these situations. Alternatively, a combination of a liquid-applied membrane with a dimpled drainage board can provide enhanced protection.
Basement Wall Condition: The existing condition of the basement walls plays a crucial role in membrane selection. If the walls are relatively smooth and uniform, sheet membranes may be the most efficient and cost-effective option. However, if the walls are cracked, uneven, or have numerous penetrations, a liquid-applied membrane may be more suitable due to its ability to conform to irregular surfaces and seal cracks effectively. In cases of severe cracking or structural damage, structural repairs may be necessary before applying any waterproofing membrane.
Budget and Longevity: The project budget and desired lifespan of the waterproofing system are also important considerations. While some membranes may offer superior performance, they may come at a higher cost. Conversely, less expensive options may require more frequent maintenance or replacement. A cost-benefit analysis should be conducted to determine the most appropriate balance between upfront cost and long-term durability. For instance, while cementitious coatings are typically the least expensive option, they may require reapplication every few years to maintain their waterproof integrity. EPDM rubber membranes, on the other hand, offer exceptional durability and longevity, but may require a higher initial investment.
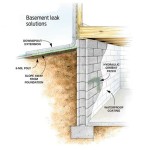
Drainage System: An effective waterproofing system should not be viewed in isolation. It must be integrated with a comprehensive drainage system to effectively manage groundwater and prevent hydrostatic pressure buildup. This may include installing a perimeter drain (French drain) around the foundation, as well as a sump pump to remove any water that accumulates in the drainage system. A well-designed drainage system significantly reduces the burden on the waterproofing membrane, extending its lifespan and improving its overall effectiveness.
Local Building Codes and Regulations: Before selecting and installing a waterproofing membrane, it is essential to consult local building codes and regulations. Some jurisdictions may have specific requirements regarding the types of membranes that are permitted, as well as the minimum standards for waterproofing performance. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in costly fines and delays.
In conclusion, the selection of the best waterproofing membrane for basement walls requires a thorough understanding of the available options, their respective strengths and weaknesses, and the specific conditions of the basement environment. By carefully considering these factors and consulting with qualified waterproofing professionals, homeowners and contractors can ensure the long-term protection and structural integrity of their basements.

Dampproofing And Waterproofing For Foundation Walls Fine Homebuilding

Foundation Waterproofing How To Waterproof Walls

Foundation Waterproofing Below Grade Walls Resisto

Advances In Spray Applied Basement Coatings Waterproof Magazine

Waterproofing Best Practices Dry Basement Solutions

Exterior Foundation Coating Products For Waterproofing Concrete Network

Waterproofing Basement Floor Slabs And Walls Waterproof Magazine

4 Best Ways To Waterproof A Basement Polyguard Architectural

Exterior Foundation Waterproofing The Best Approach

Waterproofing Your Basement Methods And Products